Summary
This system, based on SmartState, has been developed to manage clinical research participants in a time-restricted eating study focused on improving metabolic risk in postmenopausal women. The study, a collaboration between the University of Kentucky and Arizona State University, uses a state-based approach to track and support adherence to the study’s schedule. An automated texting service, driven by participant data, manages interactions and collects information, which is made accessible to researchers through a website for viewing, managing, and exporting data. Based on the start and end eating times, the system calculates a success rate for each participant. This success rate is based on a calorie intake window of 9-11 hours once a participant starts consuming calories. This system eliminates the need for manual interactions with participants and improve overall participant adherence to the study guidelines.
Datasets/Models
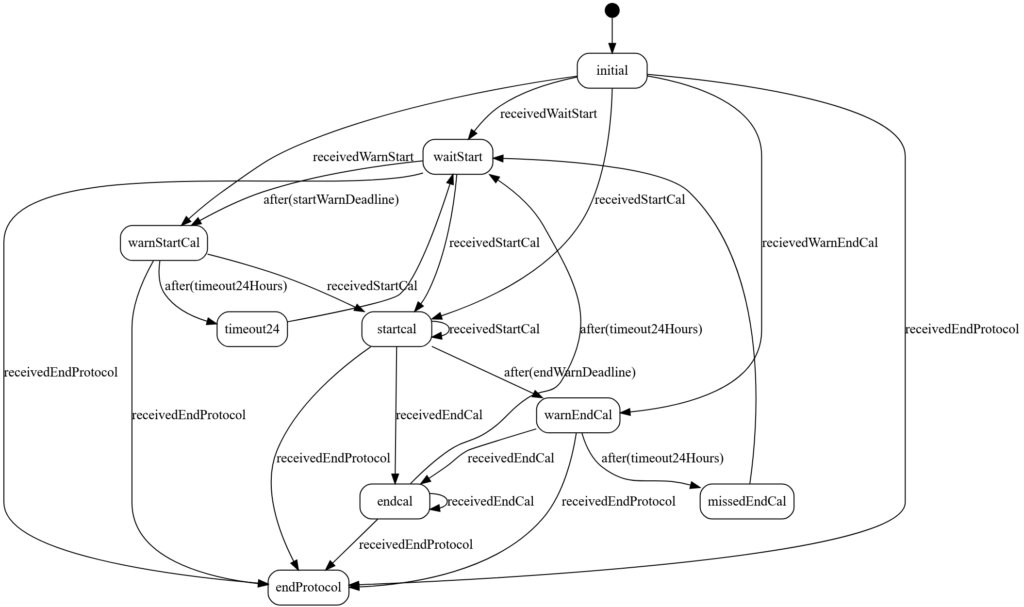
State Machine Diagram Example
The following diagram was automatically generated using UmpleOnline, a powerful online tool that not only creates intuitive state machine diagrams but also produces the corresponding code for seamless integration with our system.
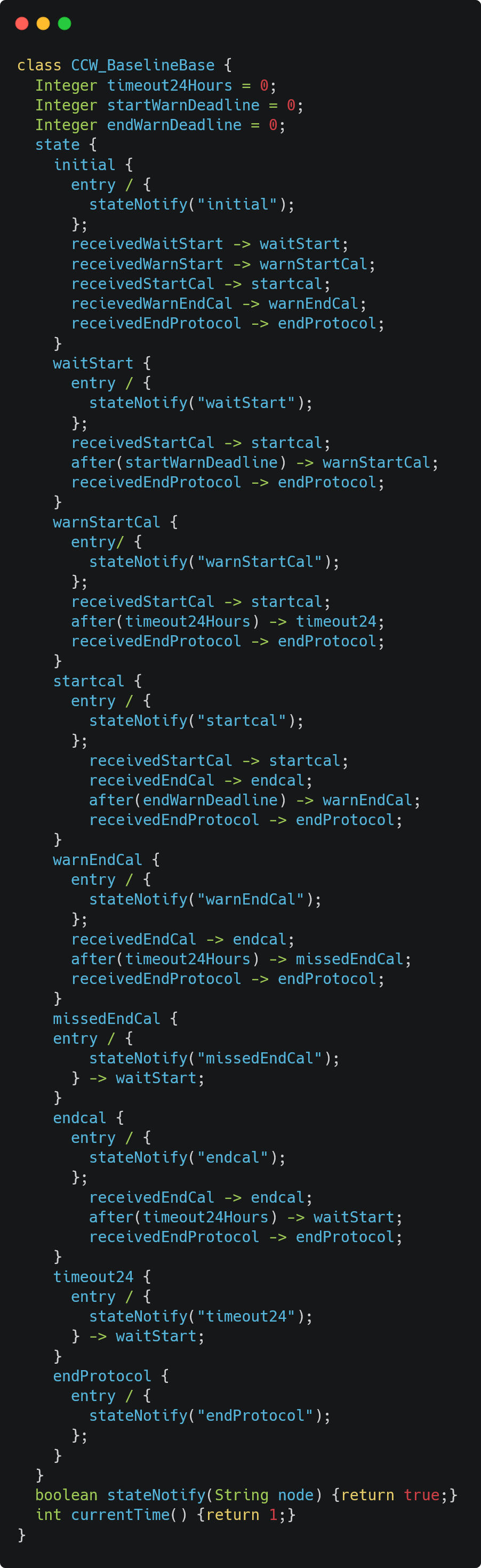
UML and Java Code Overview
Below is the Unified Modeling Language (UML) script that defines the above diagram, along with the Java code it generates. Though the UML file is just 75 lines long, it produces 607 lines of Java code, significantly speeding up development.
One of the key advantages of using state machines is the clarity they provide. Stakeholders, like researchers, can easily visualize and validate each path in the diagram, ensuring it aligns perfectly with their needs.
System Performance
From September 9, 2021 to September 12, 2024:
- Incoming Messages Received = 13,255
- Outgoing Messages Sent = 11,148
We measure the systems automatic response performance by tracking which incoming messages were not understood by the system. Of the 13,255 messages, 858 were not understood giving a percentage of 93.53% of messages accurately being understood an automatically processed by the system.
Research Study Analysis
Our text messaging time-restricted eating intervention successfully reduces daily calorie window. Participants in the TRE group reduced their calorie window an average of 3.13 h, while the control group only reduced their calorie window an average 0.2 h. TRE participants were successful in adhering to TRE on average 93% of days. All diagrams courtesy of Matt Thomas (Department of Biology, University of Kentucky).
Access
SmartState is free, open-source software and available at this link: https://github.com/innovationcore/SmartState-public
Ownership
Contact ai@uky.edu to schedule a consultation.
Resources Utilized
Developer Sam Armstrong has developed and is maintaining this project.
- 20% of Sam’s FTE for the development of the system (2 years)
- 5% of Sam’s FTE for the ongoing maintenance of the system (2023-present)

